- /
- /
- /
Voice over IP
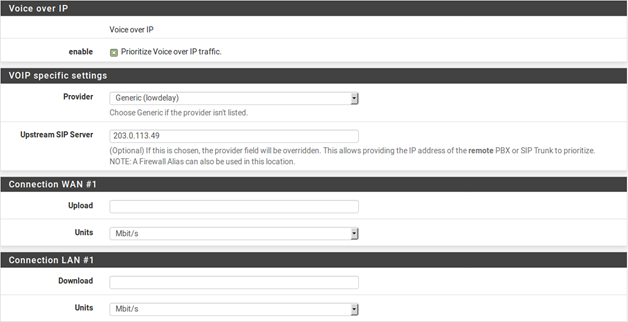
The wizard contains several options for handling VoIP call traffic, shown in Figure 108: Voice over IP. Prioritizing Voice over IP traffic sets up queues and rules to give priority to VoIP calls and related traffic. This behavior can be fine-tuned by the other settings on this step of the wizard.
Enable A checkbox to enable the VoIP settings on this step. When unchecked, the options are disabled and these queues and rules will not be added by the wizard.
Provider There are a few well-known providers including Vonage, Voicepulse, PanasonicTDA, and As- terisk servers. If the VoIP provider for this site is not in the list, choose Generic. This choice sets up rules based on the ports and protocols known to be used by these providers, rather than matching by address.
Note: This choice matches based on SIP and RTP ports, among others, therefore it can match traffic from other sources as well if they use the same ports as the selected service.
Upstream SIP Server The IP of the upstream PBX or SIP trunk, or an alias containing the IP addresses or networks for the SIP trunk(s). When set, this overrides the Provider field and will instead match traffic based on these addresses.
Note: This choice matches all UDP traffic to and from the specified address(es). In most cases this is OK, but if there are other Non-VoIP UDP-based services on the same remote address, it could match that traffic as well. Such cases are rare, however, so this option tends to be more reliable than matching by port.
WAN Connection Upload The amount of upload bandwidth to guarantee for VoIP devices. This will vary based on how many VoIP devices are on the network and how much bandwidth each session requires. This setting is used by HFSC and CBQ, and should be left blank for PRIQ.
Note: The bandwidth reservation for a service such as VoIP cannot exceed 30% of the avail- able bandwidth on the link. For example, on a 10Mbit/s link, the shaper cannot reserve more than 3Mbit/s.
LAN Connection Download The amount of download bandwidth to guarantee for VoIP devices. This setting is used by HFSC and CBQ, and should be left blank for PRIQ.
Note: The best practice is to use the remote SIP trunk or PBX address because otherwise the shaper may not be able to match traffic properly. For example, using the IP addresses of phones the shaper may only match traffic in one direction, or not at all. This is due to the way the shaper matches traffic with floating rules in an outbound direction. NAT applies before traffic is matched when exiting a WAN, so the shaper rules cannot match outbound connections based on local private IP addresses.
To use these options:
• Check Prioritize Voice over IP traffic
- Pick ONE of the following:
- Choose a Provider from the list OR
- Enter an Upstream SIP Server address or alias containing a remote SIP trunk or PBX
- Leave Upload and Download blank if using PRIQ, otherwise enter an appropriate Upload or Download value for each connection
- Click Next to proceed with the next step